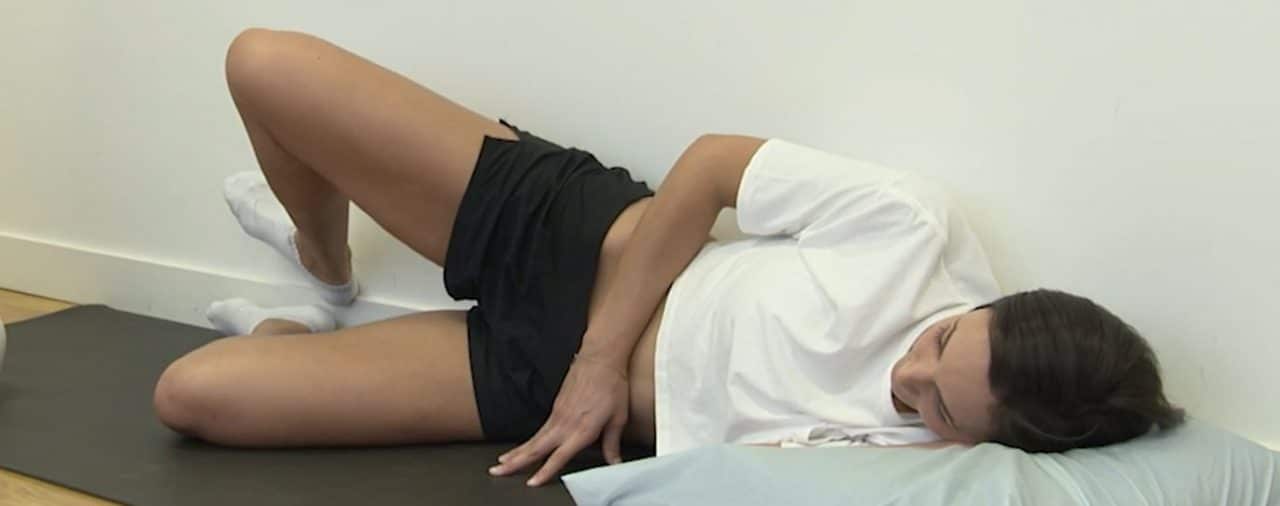
What is this exercise?
The clam is a great exercise to activate your gluteus maximus and deep external rotators of the hip and is simple to perform. A variation of this exercise can be done to activate your gluteus medius.
See link to Arabesque, Bulgarian, bridge and step up.
There are many variations that you can use to complete this exercise but in our Feel the Burn video, we focus on the most effective and efficient way to perform the exercise to activate your gluteus maximus ( GMax ) at the back.
It is important to understand that with this exercise we want to work the ( GMax ) and deep external rotators and not gluteus medius GMed / side glute).
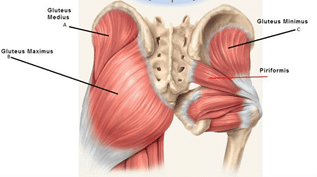
If you lift with leg and the foot, then you will find that GMed will work more and this it not what we are trying to achieve with this form of the exercise.
To ensure you achieve the best technique, you need to have support behind you. You can gain this by lying with your back flat against the wall or back of a firm couch with your shoulders back. This will help support your pelvis and spine, minimise any twisting and focus the exercise on turning the hip outwards.
Now with your feet together and your heels against the wall, lift your knee as high as possible. If you turn your foot outwards (with the heels still resting gently together) as well as lifting your knee you will get a greater activation of the GMax and deep external rotators at the back.
Repetition goal: 40+ reps or to fatigue
To increase the resistance and difficulty of the exercise you may use exercise bands around the thighs
Common Errors
I feel the outside of my leg burning > turn your foot out with your heels still touching and lift your knee higher
I feel my groin working > don’t push down on your heels as you keep them together, just have light pressure
What muscle groups does this exercise use?
Primary Activation/BURN
- Gluteus Maximus
- Deep external hip rotators
Secondary Activation
- Gluteus Medius
- TFL
Benefits
- Gluteus Maximus activation and strength
- Deep external rotators activation and strength
- Hip stability
- Pelvic stability

